Let’s recap a bit to understand the first about API before going into detail about the types of API.
In the dynamic landscape of software development, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) serve as the backbone for seamless integration and communication between different software applications. APIs act as intermediaries, allowing different software systems to interact and share data efficiently.
Types of APIs serve different purposes and cater to diverse development needs. Understanding the classification of APIs is crucial for developers to choose the right tool for their projects and maximize their functionality.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the Types of API, exploring the different types and their respective characteristics. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey in the world of programming, grasping the nuances of API classification will undoubtedly enhance your understanding of software development and empower you to build robust, interconnected applications. Let’s embark on this journey into the realm of APIs and unravel the diverse tapestry of their classifications.
- What Are APIs?
- Types of API
- Open APIs
- The API that is available for public use is known as public API. For Example, let’s take Google anyone can use Google’s API without any restriction. There is no restriction at all in open API
- Partner APIs
- Internal APIs
- Composite APIs
- Communication Level of APIS
- High-Level APIS
- Low-Level APIS
- Web service APIS
- SOAP API
- XML-RPC
- JSON-RPC
- REST
- What does stateless mean in REST?
- Conclusion
What Are APIs?
An API {Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that allow software applications to communicate with each other. APIs define methods and data structures that developers can use to interact with a service or platform, enabling them to access certain functions or specific data without having to understand the operation of the system providing those functions or data breed Simply put, you can think of an API as a messenger that takes a request from you (or from your application) and tells a system what you want it to do, then the system gives you a response back This Might include receiving data, transmitting data, or performing certain functions within a system or service. APIs are widely used in web development, mobile app development, and various other software applications that enable the integration of systems or services.
Imagine that you are at a restaurant and want to order a meal. You don’t go into the kitchen and start cooking by yourself, do you? Instead, you talk to the waiter, who then presents your order to the chef. In this case: You are either a user or a programmer. The server is like an API. The cook is like a program or service. So, the API (waiter) takes your request (order) and communicates it
Types of API
API Can be classified based on the following Parameters.
1) Ownership types of Web APIs
2) Communication level of APIs
Let’s learn in detail about both parameters to understand the types of API.
Ownership Types Of Web APIs – Types of API
Ownership types of web APIs refer to the categorization based on who develops, maintains, and controls access to the API. These classifications are essential for understanding the governance, access control, and responsibilities associated with utilizing a particular API. Here are the main ownership types:
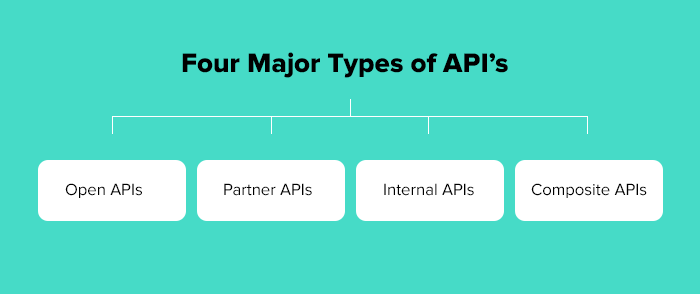
On the Ownership level, there are four main types of API:
- Open API’s
- Partner API’s
- Interna API’s
- Composite API’s
Open APIs
The API that is available for public use is known as public API. For Example, let’s take Google anyone can use Google’s API without any restriction. There is no restriction at all in open API
Some Common Examples are 3Scale, Apigee, CapitalOne, Google, IBM, Intuit, Microsoft, PayPal, Restlet, and SmartBear, etc.
Partner APIs
For Partner API some amount of rights or licenses is required so that a user can access the data. In simple words, partner APIs are those APIs that cannot be accessed publically and without permission. Normally these APIs are referred to as paid APIs so only the premium customer can access the particular data through API.
Examples of Partner APIs are Payment Gateways there APIs can only be accessed by the paid customer.
Both Open APIs and partner APIs are the tip of the iceberg because they are the most visible ones and are used to communicate beyond the boundaries of the company.
They are usually exposed to a public API developer portal that developers can access in a self-service model. While open APIs are completely open, there is an onboarding process with a specific validation workflow to get access to partner APIs.
Internal APIs
Internal API or you can say a private API can be defined as a type of API created within a company to interconnect several processes through it. The Internal API is the types of API which are used by a company for its employees. Internal API cannot be accessed by anyone outside the organization.
Composite APIs
Composite APIs are those types of APIs that combine data and different APIs on many levels. Composite API helps the running of several processes through an API in a synchronized manner.
It is a sequence of tasks that run synchronously as a result of the execution where the result of triggering a Composite API is the result of the execution and not the request that will contain the result of the execution at the request of a task. With the use of composite API, several difficult processes can run in synchronization.
Communication Level of APIS
There are three types of API on the Communication level
- High-Level API’s
- Low-Level API’s
- Web Services API’s
High-Level APIS
High-level APIs are those types of API that we use generally in REST form where programmers have a high level of abstraction; high-level API’s are created for limited functionalities only. Their usage is very much limited as per functionalities
Low-Level APIS
Low-level APIs are those types of API that have a lower level of abstraction hence they are the most detailed, which allows the programmer to manipulate functions within an application module or hardware at a granular level. Low-level APIs are used where there is a need for a detailed level of abstraction by the developer.
Web service APIS
Web APIs are the most important types of API topic of this blog. I am going to have a detailed blog about each of the subtopics. Stay tuned for the updates.
In web service APIs the classification is done on the type of communication and behavioral approach used in building APIs:
- SOAP
- XML-RPC
- JSON-RPC
- REST
Web service APIs are the type of APIs that are tiny applications that use URLs or web addresses on the internet to provide their services to desktop, mobile, web applications, and others.
SOAP API
SOAP can be abbreviated as Simple Object Access Protocol. These types of APIs are more complex than their peers. It has its communication protocol called Simple Object Access Protocol which makes it a bit more defining than REST in terms of the level of security and the approach to how messages are sent.
SOAP offers comprehensive security, built-in ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance, and retry logic for reliable messaging functionality which makes it more suitable for enterprise application that deals with banking transactions, LDAP interaction, and more.
SOAP is a standardized protocol that has only a proprietary XML format for transferring structured information that’s more function-driven. The types of API is used to send payloads which are data, type, and communication preferences.
Since SOAP uses XML to send payloads hence it requires more bandwidth. In addition to SSL, support SOAP uses WS-Security, which is great at the transport level and a bit more comprehensive than SSL.
Due significant level of security SOAP-based calls can’t be preserved. The cleanser is firmly combined with the server, having an exacting correspondence contract with it which makes it increasingly hard to make changes or updates. Cooperating with a SOAP API needs information about everything even before you can even start an association.
The cleanser has worked in ACID consistency which lessens irregularities and secures the uprightness of a database by recommending precisely how exchanges can collaborate with the database.
Corrosive is superior to information consistency models. Corrosive is utilized in auxiliary databases like Oracle’s SQL database to manage banking exchanges and stock administration in behemothic eCommerce stages.
The cleanser has an effective/retry rationale worked in and gives a start-to-finish dependability through SOAP delegates.
The utilization situation where you need to utilize SOAP API in building an application is just the craving to accomplish an elevated level of security.
The SOAP detail incorporates:
The handling model: how to process a SOAP message.
Extensibility model: SOAP highlights and modules.
Convention restricting principles: how to utilize SOAP with a hidden convention, for example, HTTP.
XML-RPC
XML-RPC (Extensible markup language – Remote Procedure Calls) is a protocol that uses a specific XML format to transfer data. XML-RPC uses minimum bandwidth and is much simpler and older than SOAP.
JSON-RPC
JSON-RPC (JavaScript Object Notation Remote Procedure Call) is a lightweight remote procedure call (RPC) protocol that utilizes JSON for data serialization and transmission over a network connection. It allows communication between different software systems, enabling clients to invoke methods or procedures on remote servers and receive responses in a structured JSON format.
Here’s a more detailed exploration of JSON-RPC:
- Simplicity and Lightweight: JSON-RPC is designed to be simple and lightweight, making it easy to implement and efficient in terms of network overhead. It uses JSON as its data format, which is widely supported and easy for both humans and machines to read and write.
- Procedure Invocation: In JSON-RPC, clients send requests to servers by specifying the method they want to invoke along with any parameters required for the method. The server processes the request, executes the specified method, and returns the result to the client.
- Request-Response Model: JSON-RPC follows a request-response model, where each request from the client triggers a corresponding response from the server. This synchronous communication pattern simplifies error handling and ensures reliable data exchange between client and server.
- Error Handling: JSON-RPC defines a standard format for error responses, allowing servers to communicate error conditions back to clients effectively. Error responses include an error code, a human-readable error message, and optional additional data for debugging purposes.
- Transport Agnostic: JSON-RPC is transport agnostic, meaning it can be used over various network protocols, including HTTP, TCP, WebSockets, and more. This flexibility allows developers to choose the most suitable transport mechanism based on their requirements and environment.
- Versioning: JSON-RPC supports versioning, allowing for backward compatibility and evolution of the protocol over time. Clients and servers can negotiate the protocol version they support, ensuring interoperability between different implementations.
- Security Considerations: Like any remote procedure call protocol, JSON-RPC implementations should consider security aspects such as authentication, authorization, encryption, and validation of incoming requests to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential security risks.
Overall, JSON-RPC offers a simple yet powerful mechanism for building distributed systems and facilitating communication between different software components. Its lightweight nature, support for various transport protocols, and ease of implementation make it a popular choice for web services, APIs, and other distributed applications. As developers continue to embrace JSON-RPC for their projects, its role in enabling seamless integration and interoperability across diverse software environments is expected to grow.
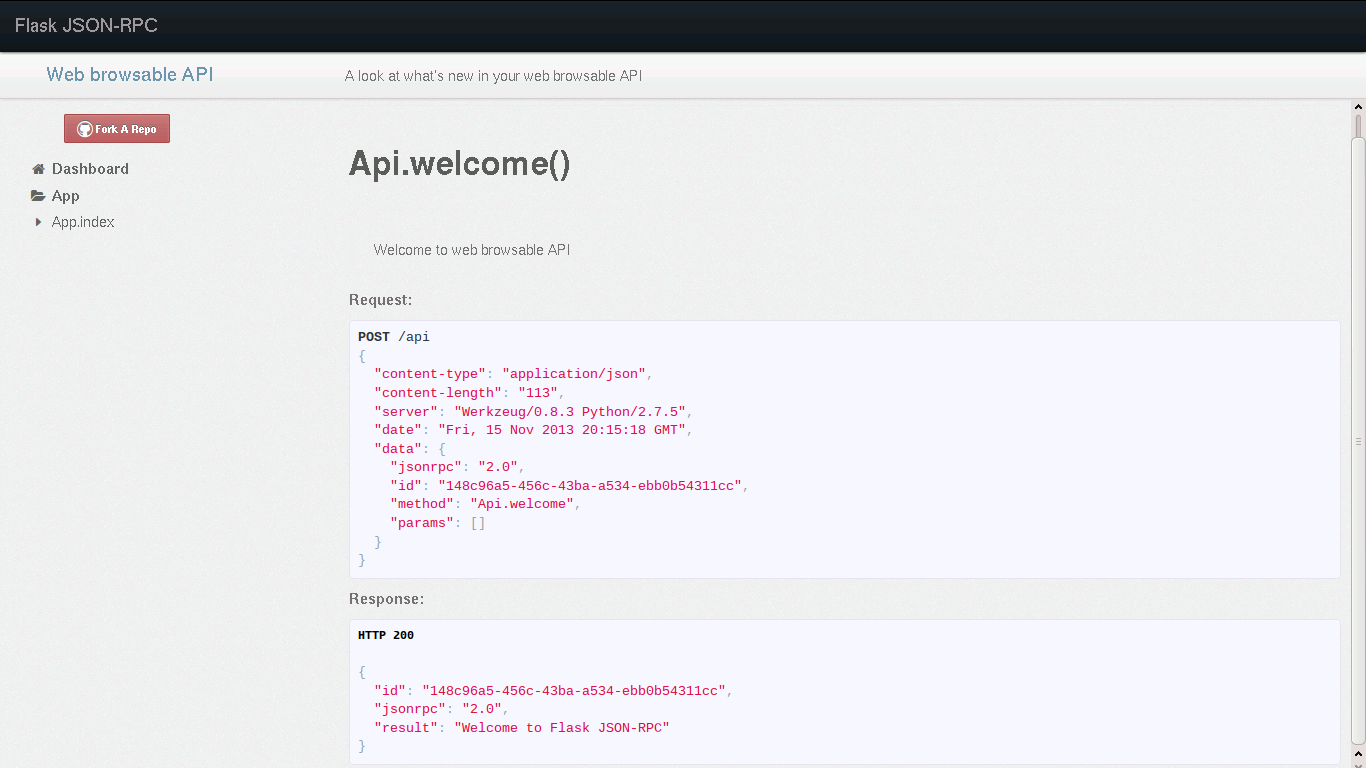
JSON-RPC (JavaScript Object Notation) is a protocol that uses JSON format to transfer data. The RPC calls are one of the methods that are used by services to communicate in a microservice architecture.
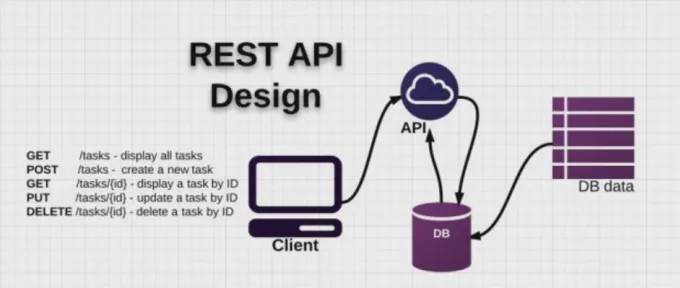
REST
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an additional information-driven engineering style that we use in building REST APIs. REST APIs depend on URIs (Uniform Resource Identifier) HTTP convention, and the utilization of JSON for an informal group, which is a super program perfect. REST APIs can be easy to fabricate and scale when contrasted with different kinds of APIs.
To be a REST API, an API must hold fast to certain structural imperatives, or standards, including:
Customer server design: the interface is isolated from the backend and information stockpiling. This takes into consideration adaptability, and for various parts to advance freely of one another.
Statelessness: no customer set is put away on the server between demands.
Cacheability: customers can store reactions, so a REST API reaction should unequivocally state whether it very well may be reserved or not.
Layered framework: the API will work whether it is discussing straightforwardly with a server, or through a delegate, for example, a heap balancer.
REST APIs encourage customer server correspondence with effortlessness.
REST APIs use SSL security which implies it can utilize HTTPS.
REST APIs utilize various information positions including plain content, HTML, XML, and JSON sending payload which is an incredible fit for information and yields more program similarity.
The utilization of easier information positions makes the payloads lighter which makes REST APIs a superior fit for a more extensive scope of uses.
REST APIs utilize a solitary uniform interface. This disentangles how applications communicate with the API by requiring they all interface similarly, through a similar entry. This has points of interest and hindrances.
REST calls can be stored.
REST APIs are best for unwavering quality and adaptability.
The reasons why you might need to fabricate an API to be RESTful is because it incorporates asset impediments, fewer security necessities, program customer similarity, discoverability, information wellbeing, and adaptability.
What does stateless mean in REST?
In REST (Representational “State” Transfer) architecture it is defined that the server does not store any state about the client session on the server side. This restriction is called Statelessness. Each request from the client to the server must contain all of the information necessary to understand the request and it cannot take advantage of any stored context on the server.
The Session state is therefore kept entirely on the client. The client is responsible for storing and handling all application state-related information on the client side. It also means that the client is responsible for sending any state information to the server whenever it is needed. So, there should not be any session affinity or sticky sessions on the server.
Conclusion
Learn more about the technical aspects of creating digital properties in our upcoming Content Management Systems blog series.
In conclusion, the classification of APIs is a fundamental aspect of understanding the diverse landscape of software development and integration. By categorizing APIs based on their characteristics, such as functionality, usage, and ownership, developers can make informed decisions when selecting the right tools for their projects. Let’s recap the key points discussed:
- Functional Classification: APIs can be classified based on their functionalities, such as RESTful APIs, SOAP APIs, GraphQL APIs, and more. Each type offers distinct features and suits different use cases.
- Protocol Classification: APIs can also be classified based on the communication protocols they utilize, such as HTTP, WebSocket, or MQTT, influencing factors like data transmission and real-time capabilities.
- Ownership Types: APIs vary in terms of ownership, including first-party APIs, third-party APIs, partner APIs, open APIs, and private APIs. Understanding ownership types helps developers navigate access control, governance, and collaboration aspects effectively.
By grasping the nuances of API classification, developers can leverage APIs more efficiently, streamline integration processes, and build robust, interconnected applications. Additionally, businesses can make strategic decisions regarding API usage, partnerships, and ecosystem development, ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in the digital landscape.
As the world of technology continues to evolve, the importance of APIs as the backbone of modern software development cannot be overstated. Embracing the diversity of APIs and their classifications empowers developers and businesses alike to harness the full potential of interconnected systems, driving progress and innovation in the digital era.
Stay tuned for more insights, updates, and best practices in the exciting realm of API development and integration. Happy coding!
If you have any questions or topics you’d like us to explore further, feel free to reach out. Thank you for joining us on this journey through the world of APIs!